Identifiers
Overview
All agents have dedicated identifiers identifying them within environments with respect to each role they are playing in each environment.
The agent identifier structure is represented by the Identifier class. This class simply stores the name of the agent, the role it is playing and the environment where it plays the role.
Identifier implements the Serializable interface because it can be put inside Message objects that are communicated through a network.
Understanding identifiers
When an agent takes a role, a corresponding unique Identifier is assigned.
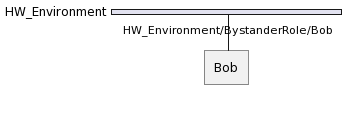
For example, when an agent called Bob takes Bystander from HW_Environment at tick 0 as follows:
...
var agent = new Agent("Bob") {
@Override
protected void setup() {
// create the bystander role for playing inside hwEnvironment
new Bystander(this, hwEnvironment);
...
}
};
...
SCOP Framework will assign this role the following Identifier:
HW_Environment/Bystander/Bob
Hereafter, the other agents can communicate with the Bystander of the Bob agent using this address through HW_Environment.
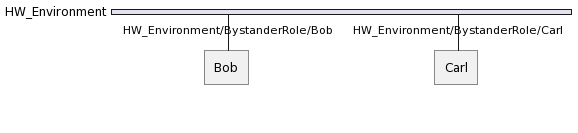
If another agent called Carl plays the same role in HW_Environment, we will have following situation:
Getting an Identifier
Agent identifiers are uniquely assigned for each role. To get the identifier of a specific role, all you need to is to call the getIdentifier() method inside one of the actions of that role.
...
public class Bystander extends Role {
...
public Action anAction() {
return new Action(this) {
@Override
public void execute() {
...
Identifier myIdentifier = getIdentifier();
...
}
};
}
}
If you are not inside that dedicated role object, but you still need to get the agent identifier, you can simply construct it by yourself:
...
Identifier myIdentifier = new Identifier("HW_Environment", Bystander.class, "Bob");
...
However, this should be done with great care, as a single mistake will unable the communication.
Having multiple identifiers
An agent can play multiple roles in the same environment and thus can have multiple agent identifiers dedicated to each role it plays in that environment.
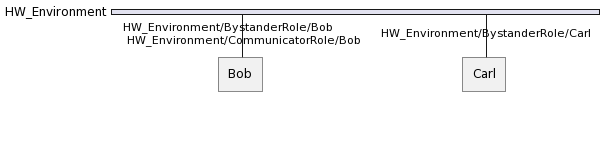
For example, supposing that Bob plays also Communicator in HW_Environment yields the following:
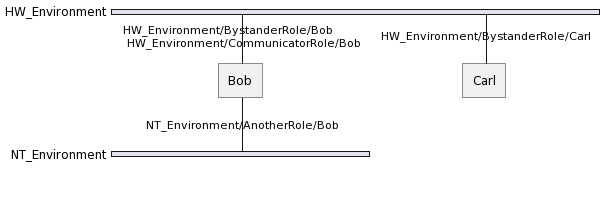
An agent can also play multiple roles in different environments and thus can have multiple agent identifiers dedicated to each role it plays in the dedicated environment.
Hence, supposing that Bob plays AnotherRole in NT_Environment yields the following situation:
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.